
- The Arc B570 shines in games like Marvel Rivals that fully utilize Intel’s XeSS Frame Generation, often surpassing both the RTX 4060 and RX 7600.
- With only 10GB VRAM and a 160-bit bus, performance drops significantly in memory-heavy game titles such as BIOHAZARD RE:4, Starfield, and F1 24, especially at higher resolutions.
- In general gaming scenarios, the B570 offers competitive performance to its peers but lacks consistency across different game engines and APIs.
- Includes full support for modern technologies like XeSS (including FG), hardware-accelerated ray tracing, and top-tier AV1 encoding, making it appealing for creators and early adopters.
- ASRock's Challenger model delivers efficient power use and quiet operation, making it suitable for compact or low-noise builds.
- At around ~$300 USD, it offers only minor savings over the more capable B580 and little advantage over the RTX 4060 and RX 7600 in terms of cost-to-performance ratio.
- While the B570 holds its own in some areas, its reduced VRAM and narrower bus make it more of a complement to the B580 than a direct competitor to NVIDIA and AMD offerings.
This is the second part of our in-depth review of Intel’s latest discrete GPU, the Intel Arc B570, which launched at 11 p.m. on January 16, 2025. In the previous installment, we provided a general overview along with basic performance metrics. This time, we’ll be putting the Intel Arc B570 through its paces in real-world gaming scenarios.
The Intel Arc B570’s launch price is approximately USD 300, including tax, about USD 33 less than the Arc B580’s. However, it comes with a GPU die that is approximately 10% smaller than that of the B580. Additionally, when it comes to VRAM—a critical factor in modern gaming—the B570 offers 10GB of GDDR6 memory, compared to the B580’s 12 GB.
Moreover, the memory bus width has been reduced from 192 bits on the B580 to 160 bits on the B570. This change could impact performance, particularly in bandwidth-demanding titles. With this in mind, we will closely examine how these hardware differences affect gameplay in today’s most demanding games. Specifically, we’ll assess how well the B570 performs in terms of resolution and image quality within its mid-$300 price range.

Performance Comparison: Intel Arc B570 vs. Intel Arc B580, RTX 4060, and RX 7600
The test setup used in this review remains identical to our previous configuration. The Intel Arc B570 is represented by ASRock’s factory overclocked model, the Intel Arc B570 Challenger 10GB OC, while the Arc B580 is the Intel Limited Edition variant. For comparative analysis, we’ve also included the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 (referred to as RTX 4060) and the AMD Radeon RX 7600 (RX 7600).
The system utilizes an Intel Core Ultra 9 285K processor and runs on Windows 11 (24H2). Graphics drivers were kept consistent with our prior testing: NVIDIA’s GameReady Driver 566.36 and AMD’s Adrenalin 24.12.1. However, for Intel Arc, we updated to the latest post-launch drivers—versions 101.6458 and 101.6257 —to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
System features such as Resizable BAR, Secure Boot, Memory Integrity, and HDR are all enabled. The display was set to a refresh rate of 144Hz for consistent testing across all scenarios.
| Testbed Environment | |
| CPU | Intel Core Ultra 9 285K (24 cores/24 threads, up to 5.7GHz) |
| CPU Cooler | EKWB EK-Nucleus AIO CR360 Lux D-RGB (Simple water cooling, 360mm radiator) |
| Motherboard | ASRock Z890 Taichi (Intel Z890, BIOS 2.22.AS03) |
| Memory | ADATA LANCER RGB DDR5 AX5U6400C3216G (16GB x 2, DDR5-6400) |
| Video Cards | Intel Arc B580 Limited Edition (12GB GDDR6), ASRock Intel Arc B570 Challenger 10GB OC (10GB GDDR6), MSI GeForce RTX 4060 VENTUS 2X BLACK 8G OC (8GB GDDR6), AMD Radeon RX 7600 Reference Card (8GB GDDR6) |
| Storage | Crucial T700 CT2000T700SSD3 (2TB M.2 SSD, PCIe 5.0), Silicon Power PCIe Gen3 x4 P34A80 SP002TBP34A80M28 (2TB M.2 SSD, PCIe 3.0) x3 |
| Power Supply Unit | ASRock TC-1300T (1300W, 80 PLUS TITANIUM) |
| OS | Microsoft Windows 11 Pro (24H2) |
All frame rate data across the tested games was captured using CapFrameX, but with a key adjustment: instead of relying on the traditional “MsBetweenPresents” metric, we used the newer “MsBetweenDisplayChange” measurement standard. This change is essential for accurately evaluating frame generation in environments utilizing technologies such as Intel’s XeSS Frame Generation (FG), and will also be critical for testing upcoming NVIDIA GeForce RTX 50 series GPUs with DLSS MFG (which we have not yet had access to).
While average frame rates remain relatively consistent between the two metrics, the difference becomes significant when assessing display output smoothness. The “MsBetweenPresents” method does not account for actual display refresh behavior, which can lead to misleading stutter analysis. In contrast, “MsBetweenDisplayChange” provides a more accurate representation of perceived stuttering and overall frame pacing.
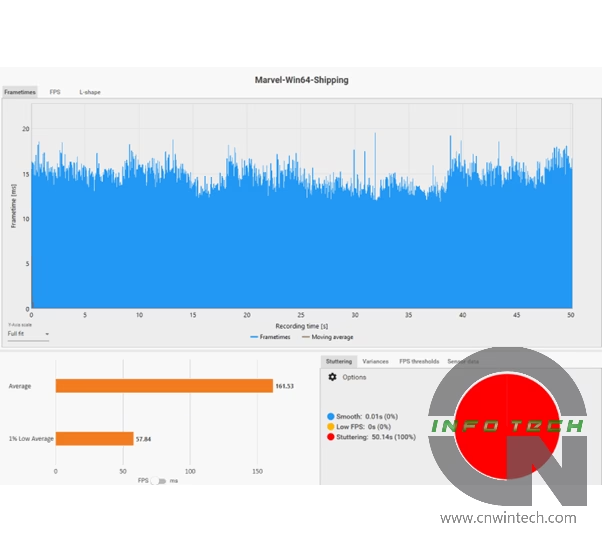
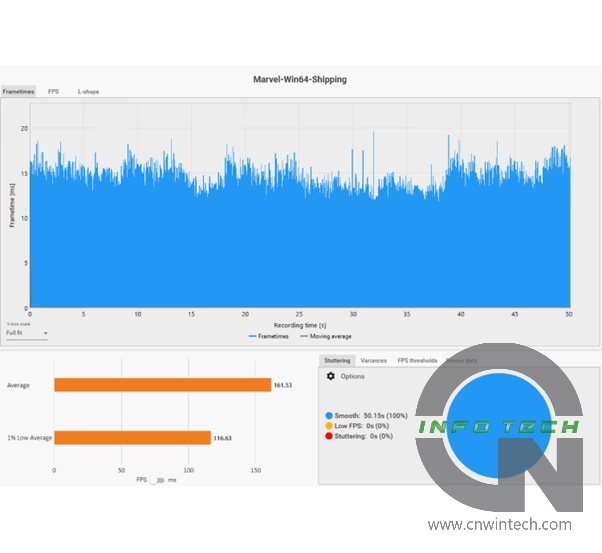
In addition to frame rate measurements, we also used HWBusters’ Pownetic v2 to measure the total board power consumption (TBP) of each graphics card during benchmark runs. By combining this data with average frame rate values, we calculated the “frames per 10W”—a useful metric for evaluating energy efficiency and overall performance per watt.
A significant drop in power consumption relative to performance may indicate issues such as software optimization problems, driver inefficiencies, or GPU bottlenecks under certain workloads.
Overwatch 2 Performance Analysis
In Overwatch 2, testing was conducted at “Epic” image quality with the render scale set to 100% and frame rate capped at 600 FPS. FSR 2 was disabled (RS = 100%). Frame rates were measured during a bot match on the “Eichenwalde” map.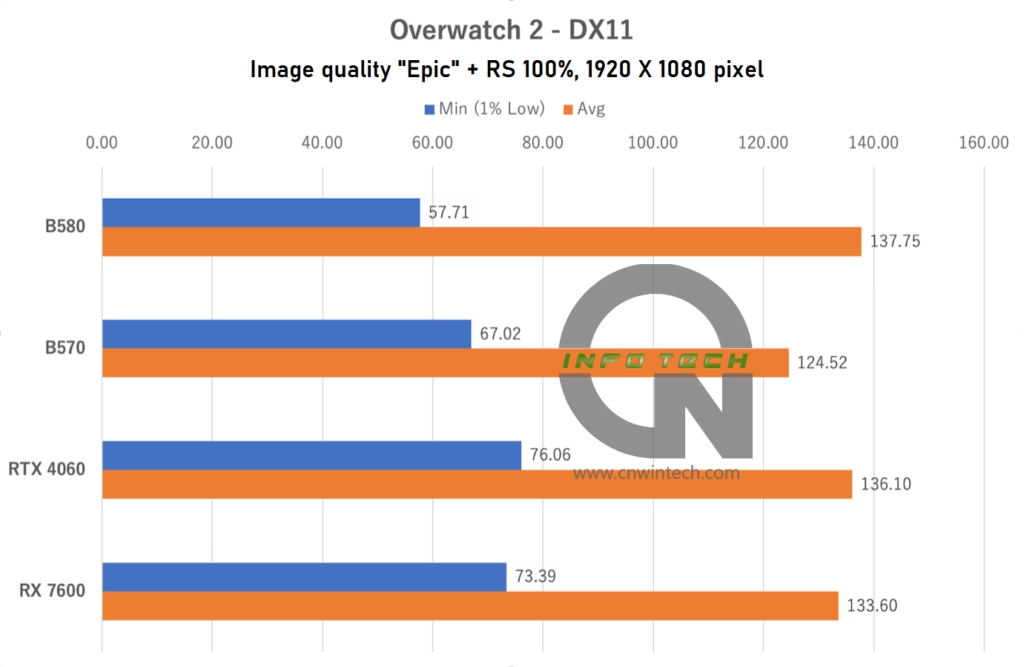
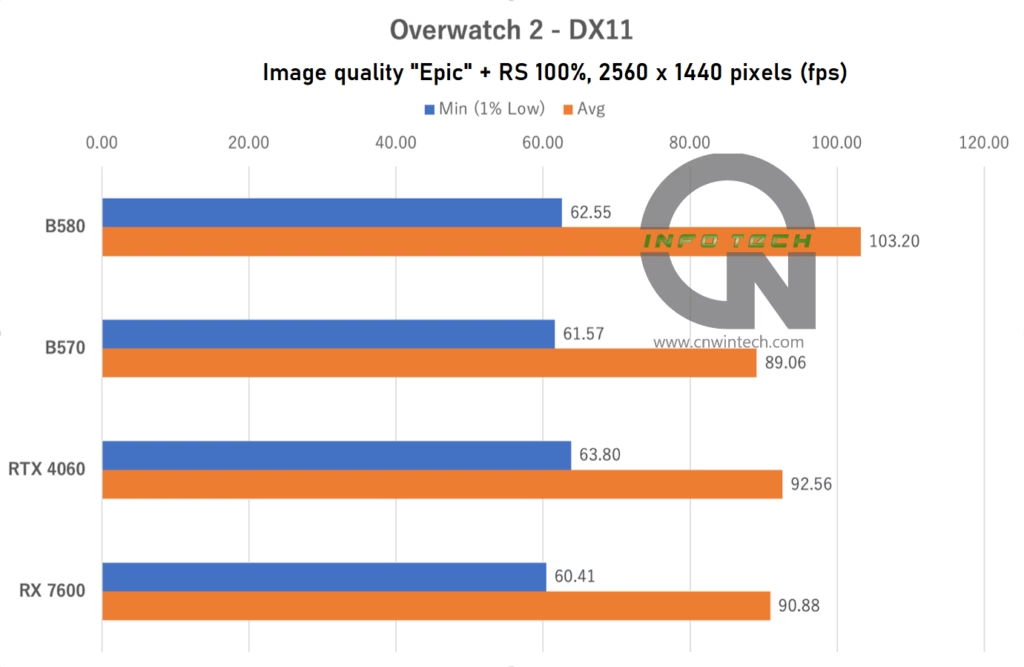
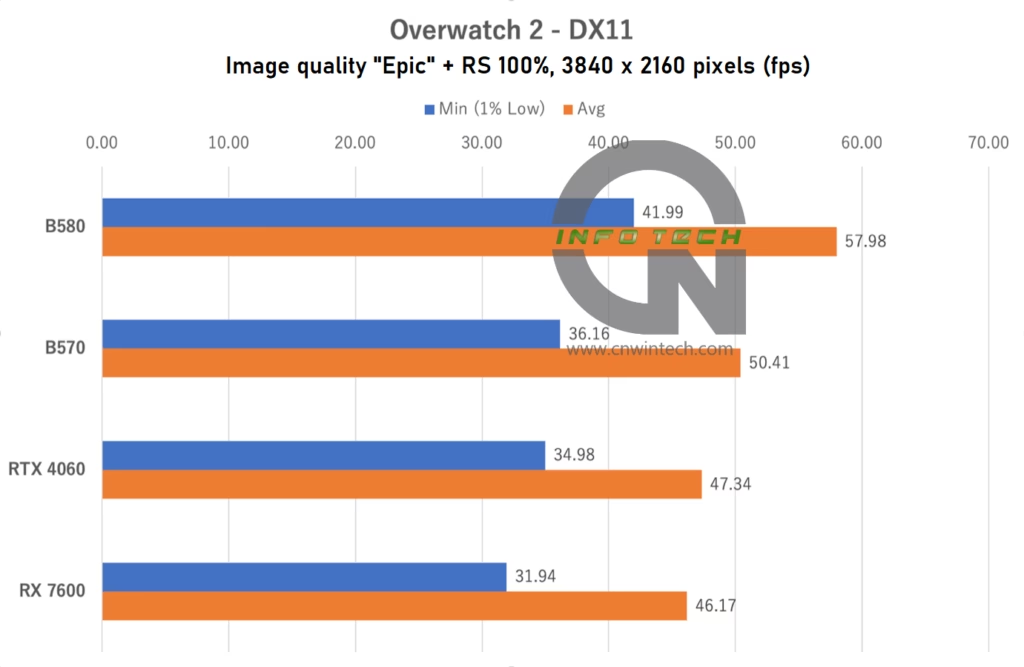
At Full HD (1080p), the Intel Arc B570 falls short of both the NVIDIA RTX 4060 and AMD RX 7600, showing an unimpressive performance profile. However, as resolution increases, its performance improves steadily. By the time it reaches 4K Ultra HD, the B570 outperforms the RTX 4060—a likely result of its superior VRAM configuration and wider memory bus compared to the B580.
That said, in more typical use cases—namely, 1080p and WQHD (1440p)—where the B570 is expected to compete most actively, it fails to gain a clear advantage over current-gen GPUs. This further underscores the strength of the higher-tier B580 model, which maintains a consistent lead without compromising on memory or bandwidth.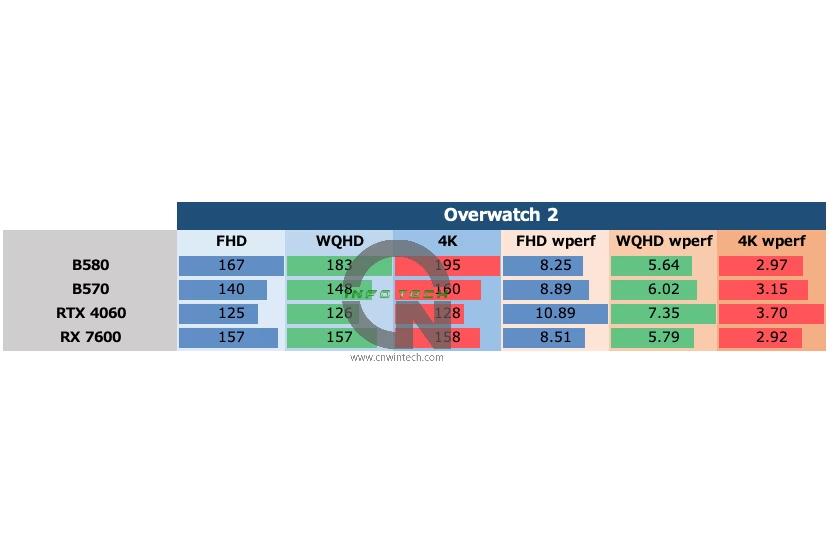
Power Consumption and Efficiency
The Intel Arc B570 demonstrates commendable power efficiency, drawing up to 35W less than the B580 under load. The trend in power draw decreases with lower resolutions, similar to what we observed with the B580, indicating stable behavior across workloads.
Compared to the RTX 4060, the B570’s absolute TBP is slightly higher, but the difference is marginal and not significant enough to raise concerns. In terms of energy efficiency—measured as frames per 10W—the B570 performs competitively, especially at higher resolutions where its architectural strengths are more fully utilized.
Call of Duty: Black Ops 6 Performance Analysis
For Call of Duty: Black Ops 6, we used the latest installment in the series with image quality set to “Extreme”. While the game supports frame generation technologies such as DLSS and FSR 3, we opted not to enable them due to the game’s strong eSports focus, ensuring our testing reflects real-world competitive performance. Frame rates were measured using the in-game benchmark playback tool.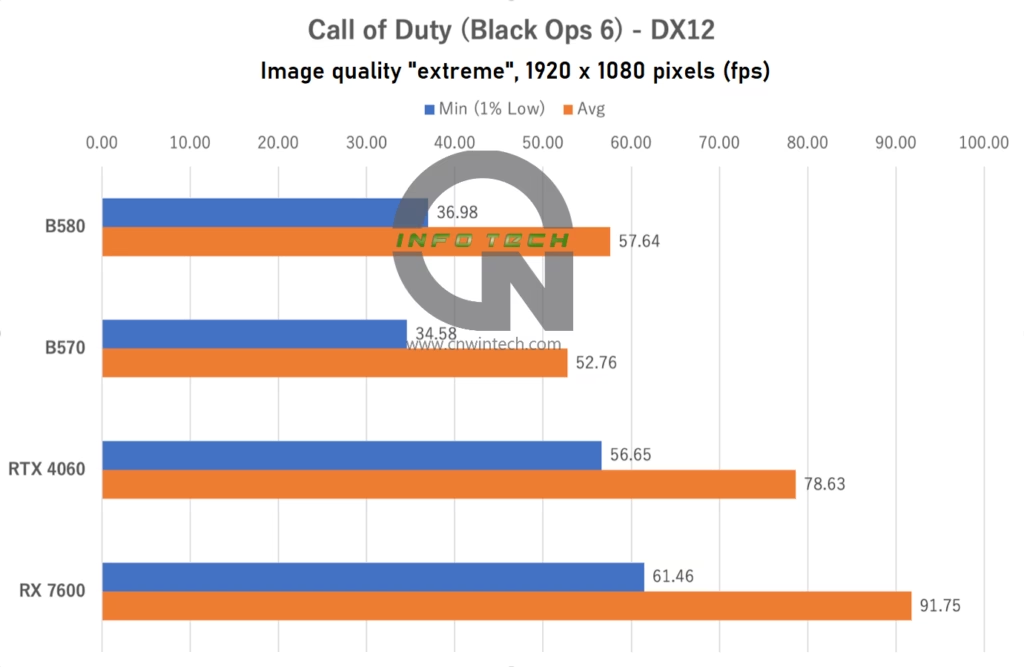
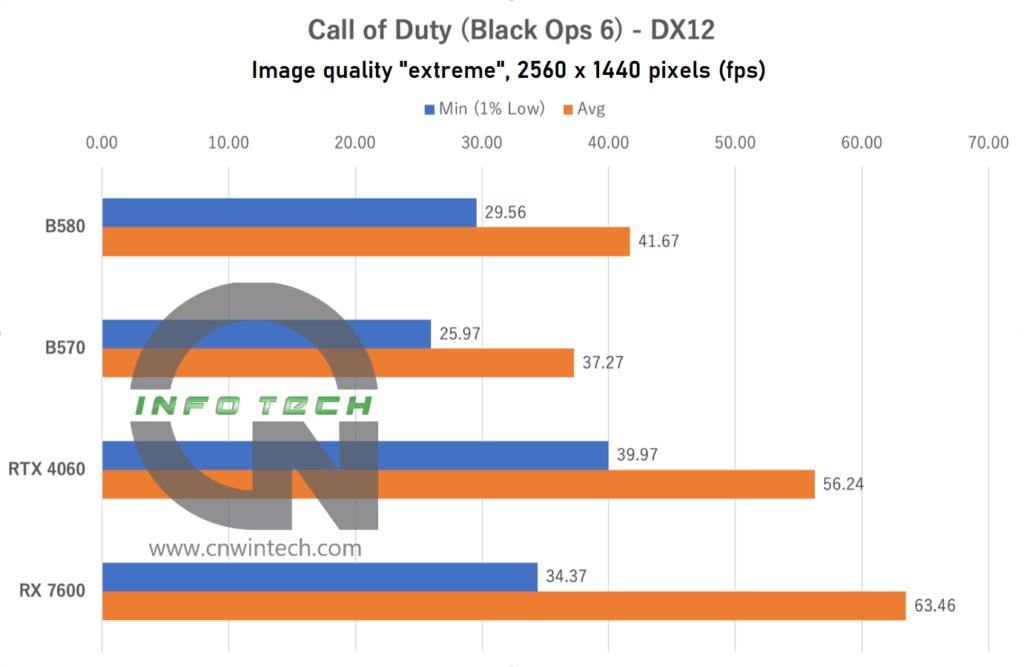
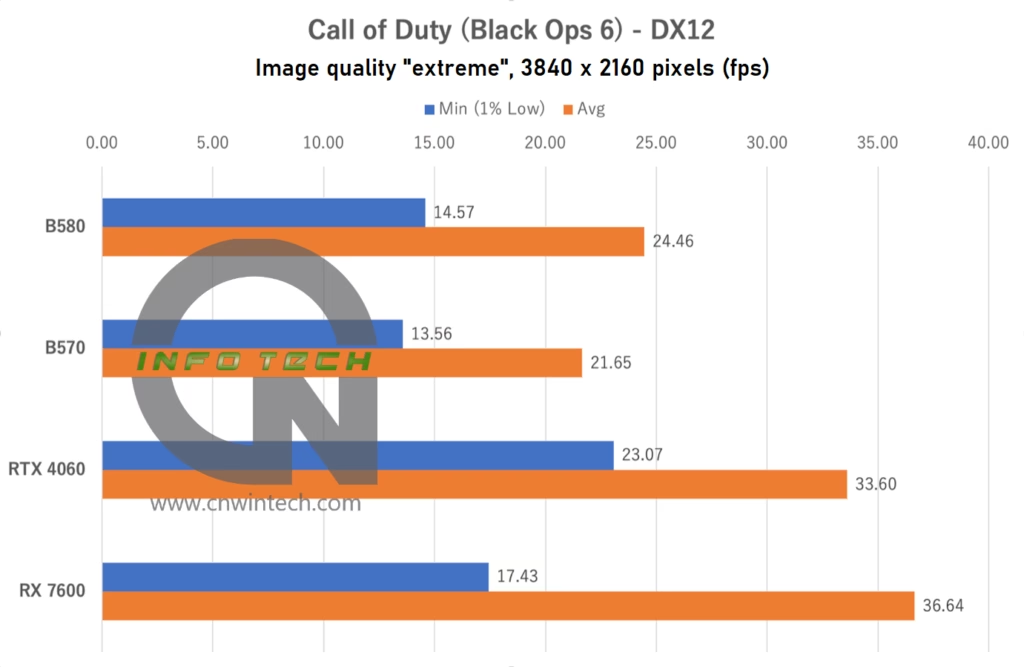
In this title, the Intel Arc B570 significantly lags behind the NVIDIA RTX 4060. Even after swapping out the OS and CPU configuration, the performance gap remains unchanged. Another notable takeaway is the impressive performance jump demonstrated by the AMD Radeon RX 7600 compared to the initial review of the Arc B580.
When we first reviewed the Arc B580 last year, we speculated that driver maturity and game-specific optimization might be limiting its performance. However, with no significant improvements observed since the start of this year, it appears this underperformance is more closely tied to how the Call of Duty engine (likely based on the IW engine) interacts with the Arc GPU architecture.
There is still hope, as seen with the RX 7600, which showed stronger results over time through driver updates. Perhaps one day, Intel Arc will deliver better performance in this title as well.
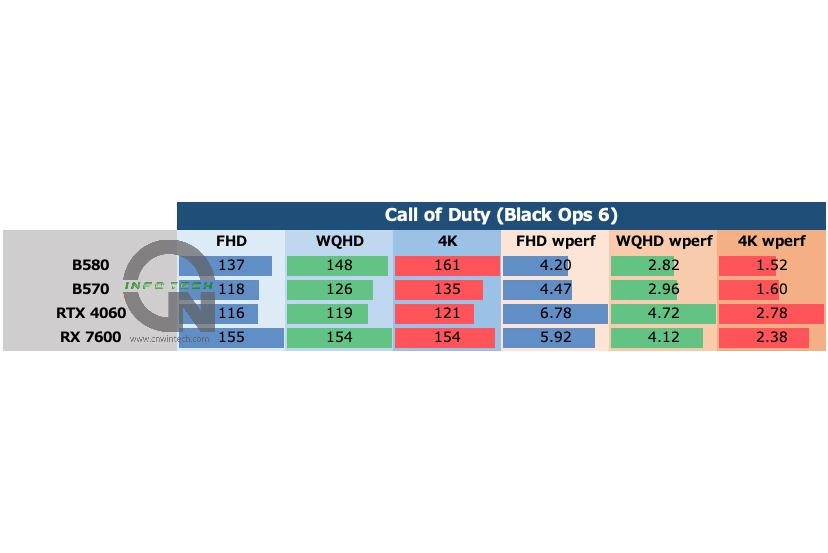
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Interestingly, the Arc GPUs show much lower TBP in Black Ops 6 compared to Overwatch 2. The RTX 4060 and RX 7600 also see a slight drop in power consumption, but not nearly to the extent observed with the Arc GPUs.
This suggests that the Arc GPU may be bottlenecked in this particular workload, possibly struggling with how the game translates shader instructions or handles intermediate language translation to GPU code. As a result, the GPU doesn’t reach full utilization, leading to lower power draw despite delivering lower frame rates.
Marvel Rivals Performance Analysis
Marvel Rivals is one of the few titles currently supporting Intel’s XeSS Frame Generation (XeSS FG), which is available on the Arc B-series GPUs. For this test, image quality was set to “Best” with upscaling options (DLSS / FSR 3 / XeSS) configured to “Quality” mode, and frame generation enabled across all platforms. Frame rates were measured while navigating a predefined path in the game’s training grounds, ensuring consistent conditions for comparison.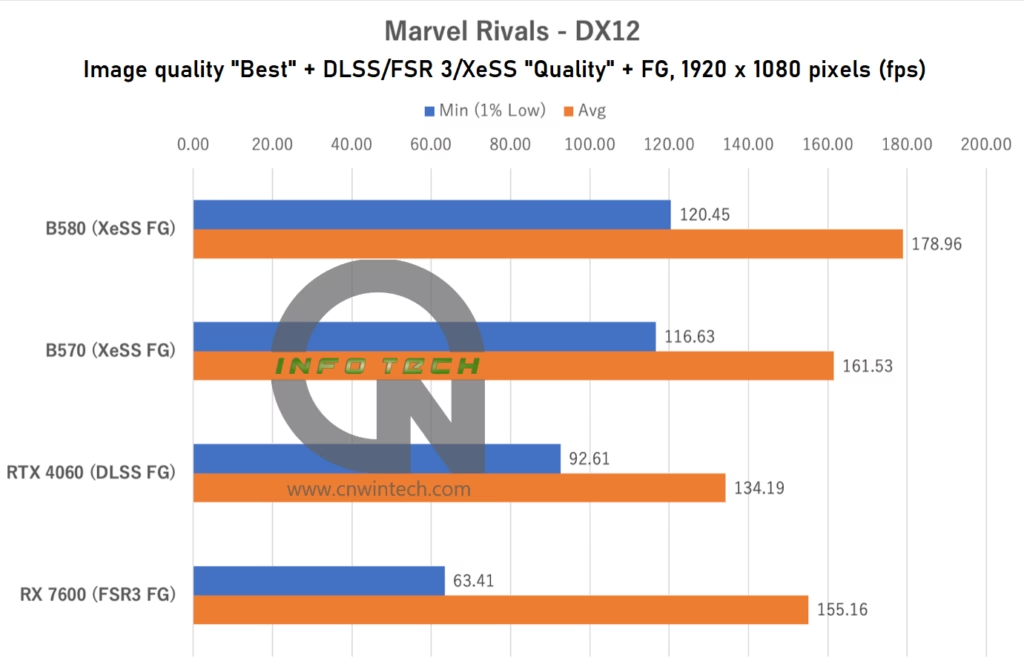
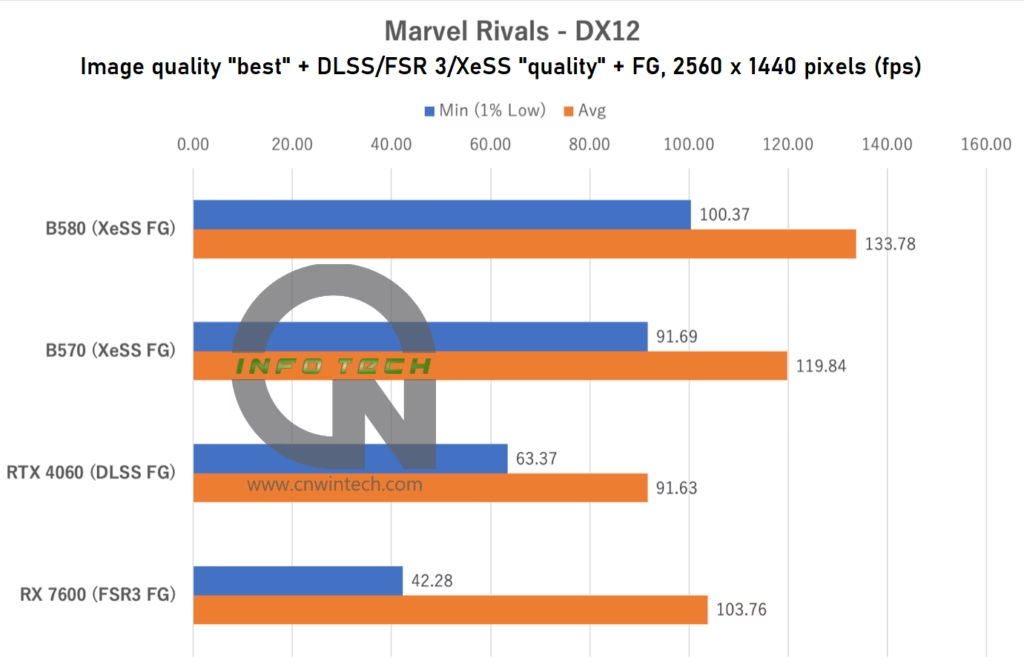
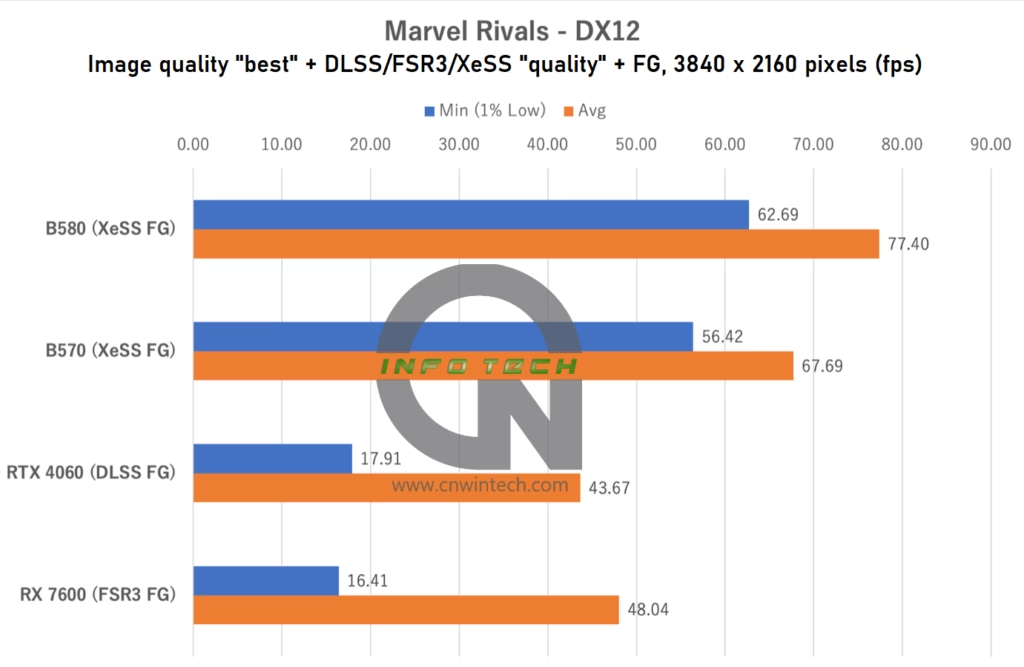
As expected from an Intel-promoted XeSS FG showcase title, the Arc GPUs deliver strong performance in Marvel Rivals. The Intel Arc B570, which previously struggled in titles like Overwatch 2, clearly outperforms both the NVIDIA RTX 4060 and AMD RX 7600 in this optimized environment.
At Full HD (1080p), the B570 achieves average frame rates approximately 20% higher than the RTX 4060. More importantly, its minimum frame rate is also excellent, contributing to a consistently smooth gaming experience without noticeable dips or stutters.
While the RX 7600 delivers a solid average frame rate, it suffers from lower minimums, especially under heavy load, leading to a less stable and occasionally jarring visual experience. This may be attributed to the RX 7600’s relatively narrow memory bus, which appears to become a bottleneck in this particular workload. Interestingly, even the RTX 4060, with its GDDR6X-like memory compression techniques, manages better low-frame performance than the RX 7600.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
The Intel Arc B570 demonstrates slightly better energy efficiency compared to the Intel B580, particularly at 1080p and 1440p resolutions. It manages to deliver high frame rates while maintaining reasonable power consumption, making it a compelling option for users prioritizing performance-per-watt.
This efficiency becomes especially valuable in games like Marvel Rivals, where the driver and architecture work harmoniously with the game engine and XeSS FG to reduce GPU workload and optimize rendering pipelines.
F1 24 Performance Analysis
F1 24 is another game that supports Intel’s XeSS Frame Generation (XeSS FG), making it a relevant title for evaluating the Arc B-series’ capabilities. For testing, image quality was set to “Ultra High”, with 16x anisotropic filtering enabled. Upscaling options (DLSS / FSR 3 / XeSS) were all configured to “Quality” mode, with frame generation activated.
Frame rates were measured using the in-game benchmark playback on the “Monaco” track under wet conditions—a demanding scenario due to complex weather and lighting effects.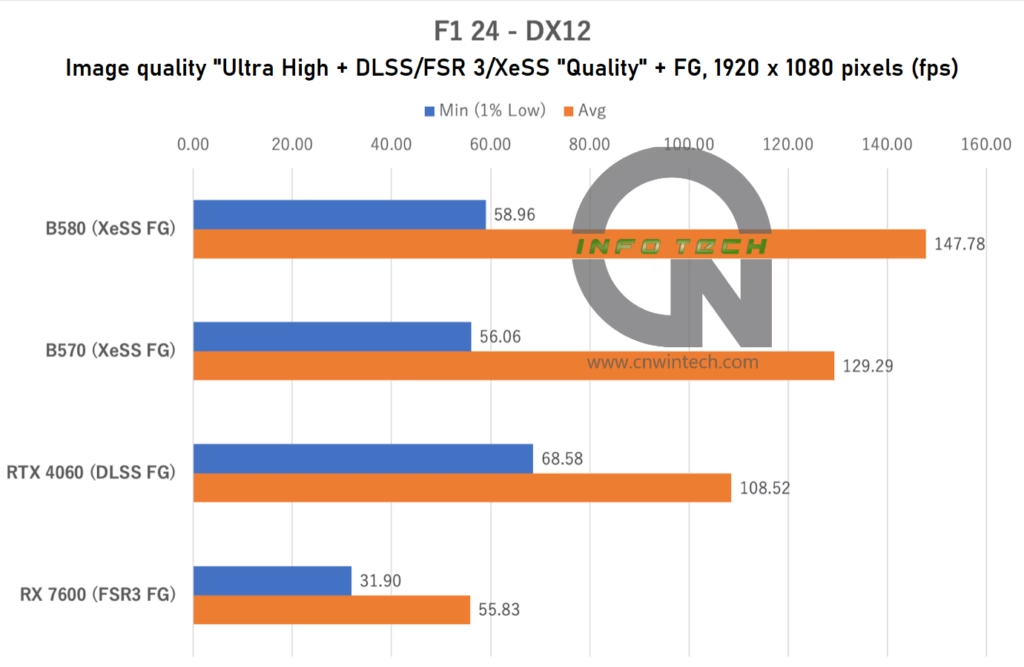
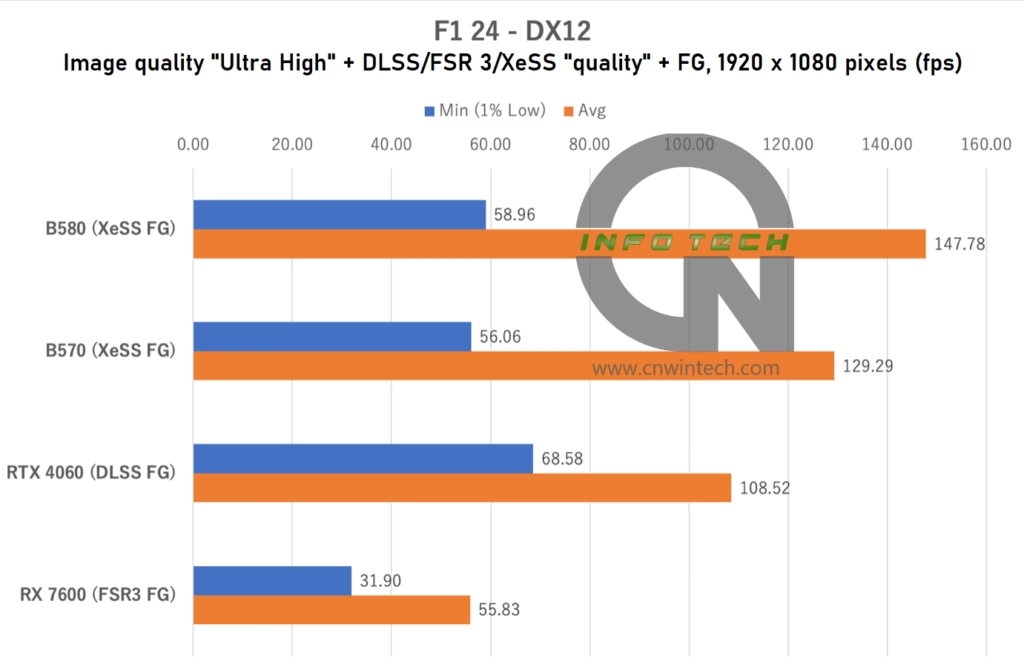
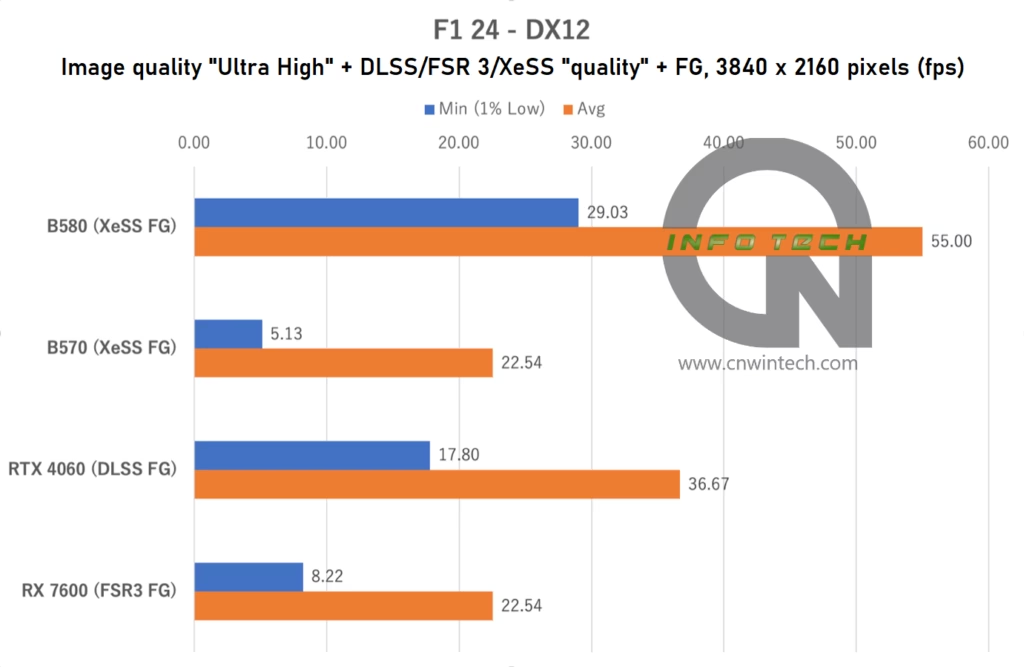
While F1 24 does support XeSS FG, its benefits are less pronounced compared to what we saw in Marvel Rivals. Although average frame rates with XeSS FG enabled are notably higher than those achieved using DLSS FG or FSR 3 FG, the minimum frame rates tend to dip more frequently, introducing occasional stutters during rendering.
At 1080p and 1440p, the Intel Arc B570 performs slightly behind the Intel B580, which is expected given the Intel B580’s superior VRAM and wider memory bus. However, at 4K resolution, the Intel B570 shows clear signs of being memory-constrained—likely due to its 10GB VRAM limit and narrower 160-bit bus. This results in a sharp performance drop, indicating that the Intel B570 isn’t ideally suited for high-bandwidth 4K gaming.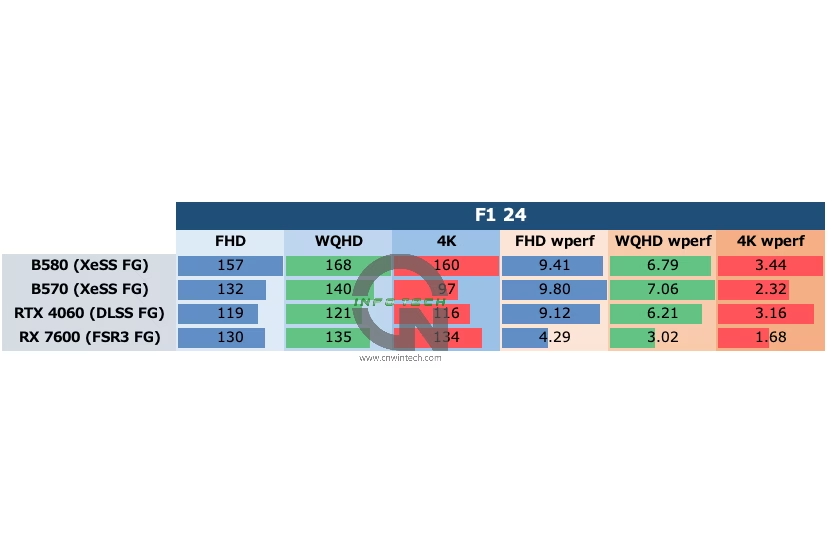
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Interestingly, the RX 7600 shows a significantly lower TBP in this title compared to Call of Duty, stabilizing around 130W. This suggests that the GPU may be bottlenecked or struggling to fully utilize its available compute resources under these specific workload conditions.
Similarly, the Intel Arc B570 performs reasonably well at 1080p and 1440p, but becomes overwhelmed at 4K. It not only shows declining performance but also fails to increase power draw accordingly, indicating a potential stall in GPU utilization rather than a thermal or power limitation.
Starfield Performance Analysis
In Starfield, image quality was set to “Ultra” with 16x anisotropic filtering enabled. The RTX 4060 utilized DLSS “Quality” mode with DLSS FG enabled. Other GPUs used FSR 3 FG at a render scale (RS) of 67%, which is roughly equivalent to “Quality” upscaling.
Frame rates were measured during exploration of the MAST district in New Atlantis—an open-world area with dense textures and dynamic lighting.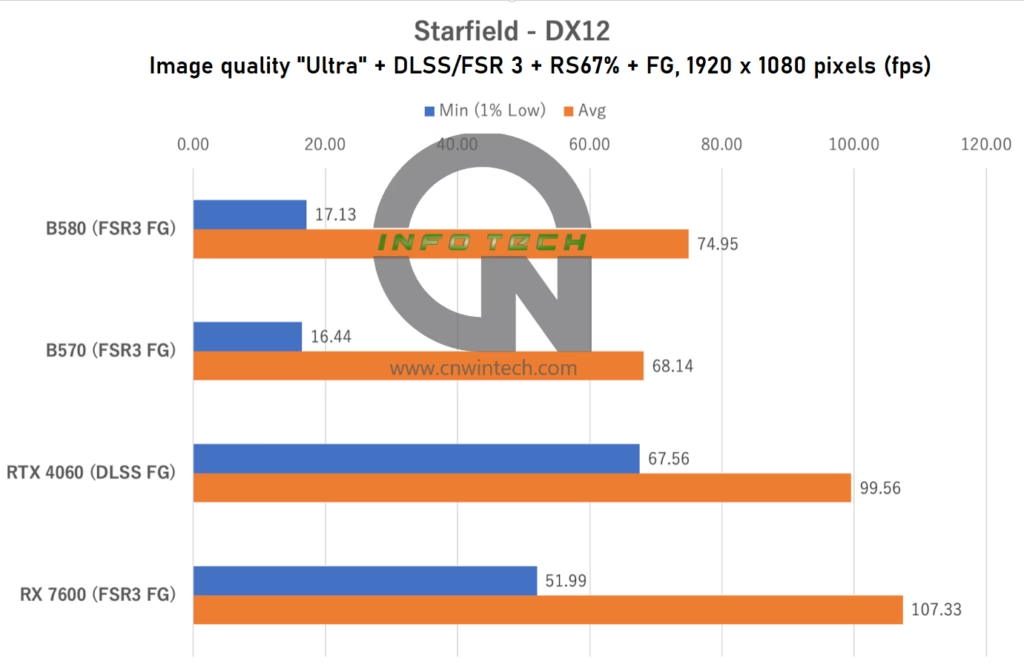
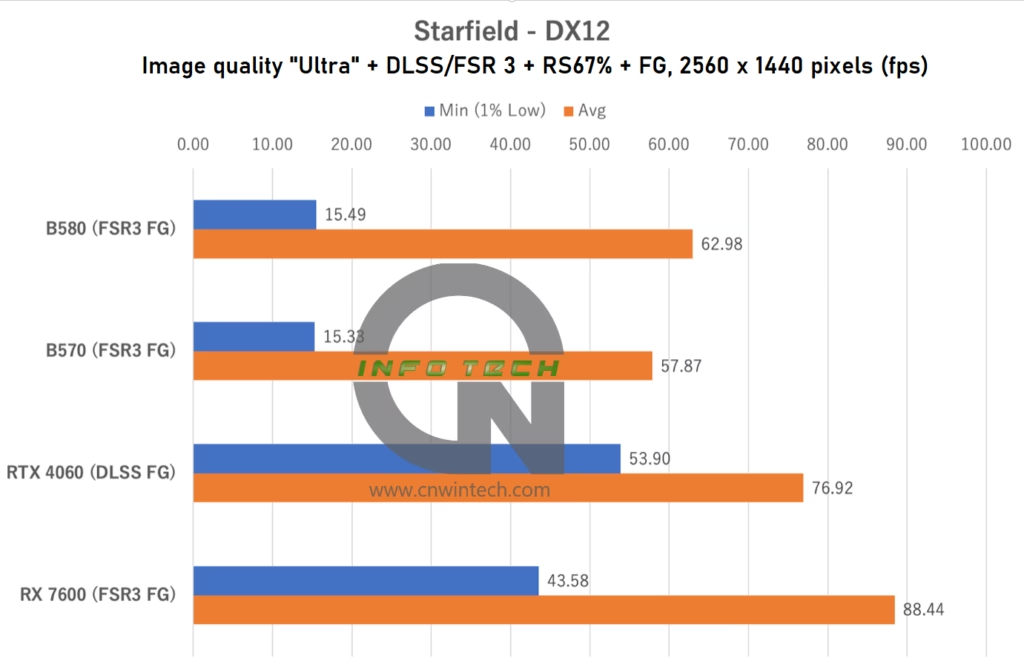
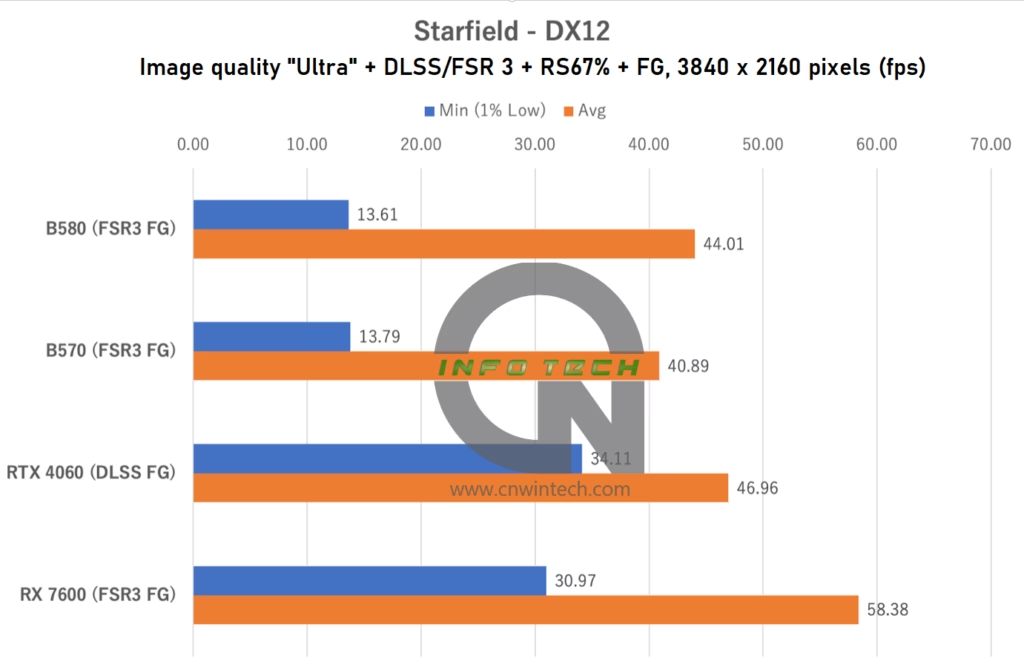
Both the Intel Arc B580 and Intel Arc B570 showed a significant drop in minimum frame rates compared to previous tests. This is especially notable because, in earlier evaluations using the Intel Arc B580, we observed better low-frame performance. In this test environment, however, both Arc models struggle to maintain smoothness, despite relatively stable average frame rates.
It’s worth noting that system configuration changes, such as switching from the Core i9-14900K to the Core Ultra 9 285K, and upgrading Windows 11 from 23H2 to 24H2, could have influenced performance. However, the NVIDIA RTX 4060 and AMD RX 7600 maintained or slightly improved their performance under these new conditions.
This raises the possibility of a compatibility or optimization issue between the Arc drivers and the combination of the Core Ultra platform and Windows 11 24H2. While further investigation is needed, the current data suggests that Intel may still need to refine its software stack for optimal performance in certain environments.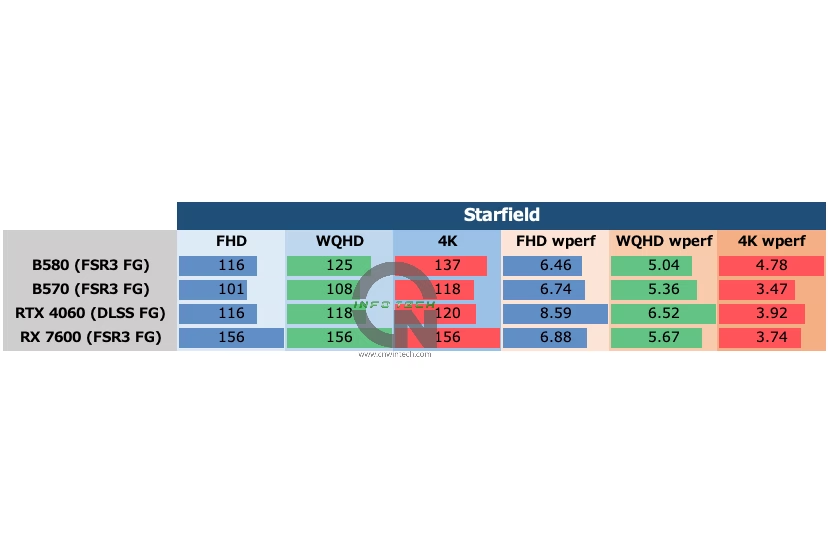
Power Consumption and Efficiency
The power consumption data for the Intel Arc B580 and Intel Arc B570 in Starfield reveals a concerning trend: despite low TBP values, performance remains subdued. This suggests that the GPU is not being utilized to its full potential—essentially, it’s not doing the required workload efficiently.
In other words, the Arc GPUs are consuming less power not because they’re efficient, but because they’re underutilized or bottlenecked somewhere in the pipeline. This could be due to driver inefficiencies, game-specific shader compilation issues, or poor CPU–GPU communication in this particular environment.
This pattern further supports the earlier hypothesis that Intel’s current software stack may not be fully optimized for the combination of the Core Ultra 9 285K CPU and Windows 11 24H2, at least in titles like Starfield. Until these issues are addressed through driver updates, users should expect inconsistent performance in certain workloads, even when the hardware appears to be capable on paper.
Cyberpunk 2077 Performance Analysis
Cyberpunk 2077 remains a demanding title and a staple for GPU benchmarking. While it supports Intel’s XeSS Super Resolution (SR), it does not yet support XeSS Frame Generation (FG). However, the game gained support for AMD’s FSR 3 Frame Generation late last year—an important development that warranted re-testing under our current configuration.
For this test, image quality was set to Ray Tracing: Ultra, with upscaling enabled at “Quality” mode via either DLSS (on NVIDIA) or FSR 3 (on AMD/Intel). Frame generation was also activated where supported. Performance was measured using the in-game benchmark playback tool.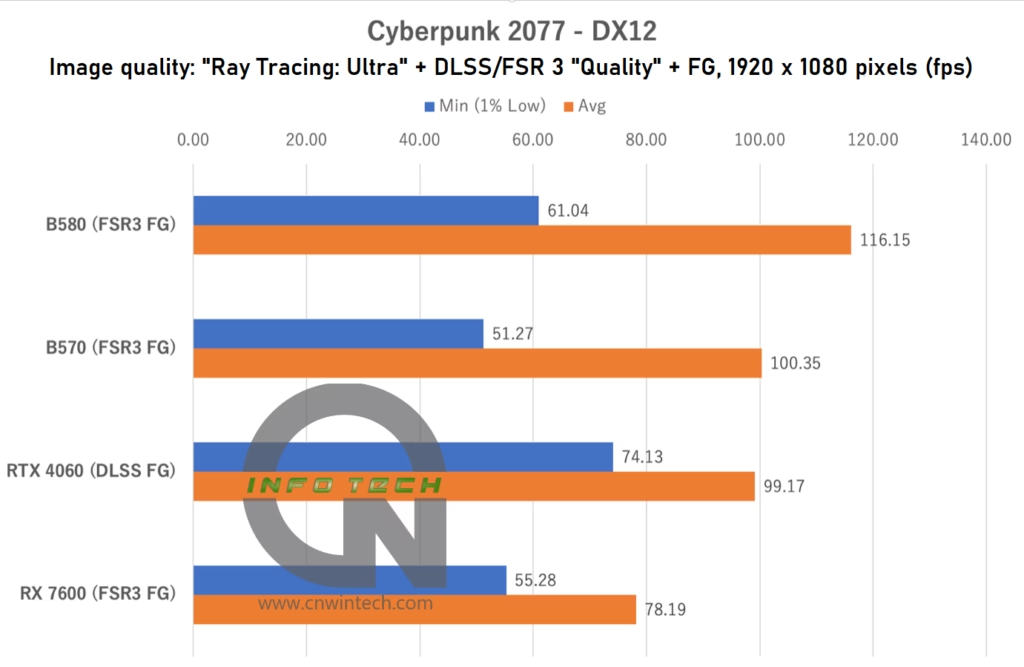
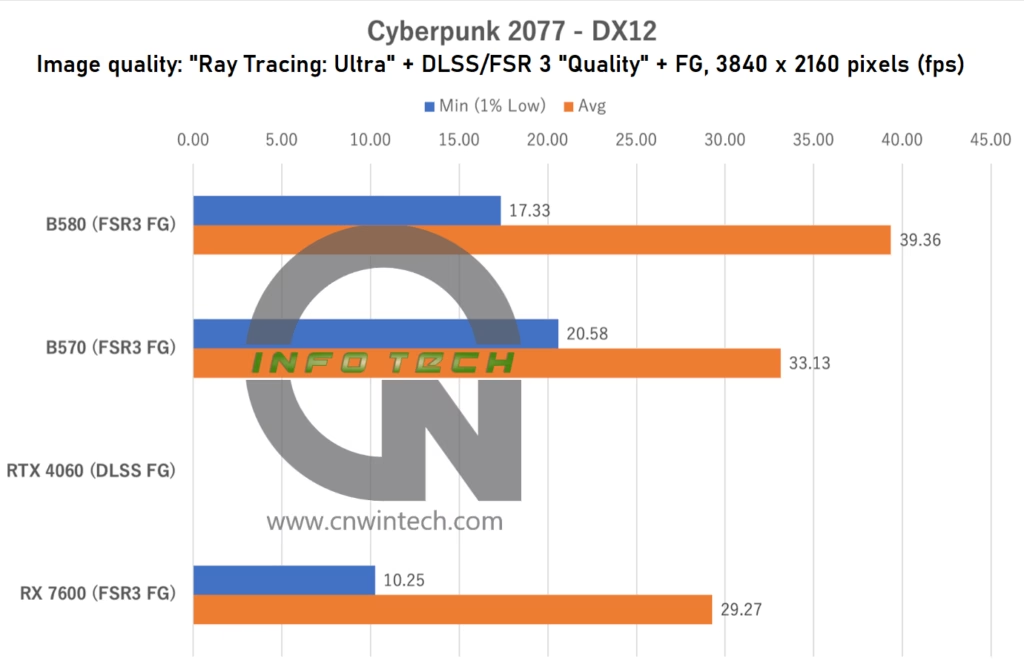
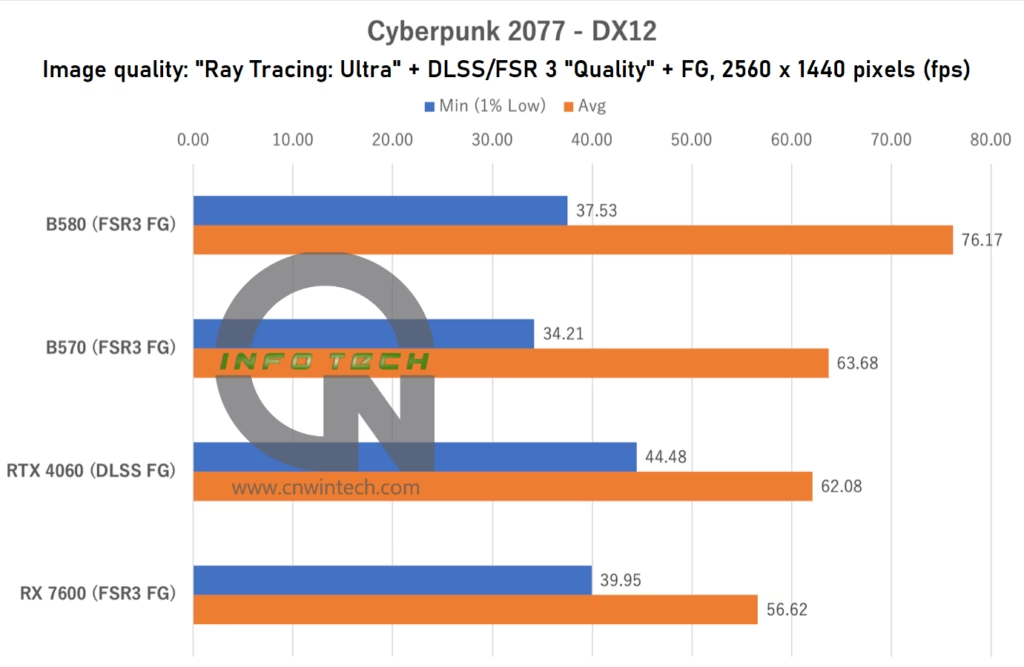
In this setup, the Intel Arc B570 delivers nearly identical performance to the RTX 4060 when using DLSS FG, despite relying on FSR 3 instead. While FSR 3 in Cyberpunk 2077 lags slightly behind DLSS in terms of visual fidelity, particularly in motion handling, the frame rate results suggest that the Intel Arc B570 can still hold its own in one of the most graphically intensive games available today.
That said, actual gameplay requires some adjustments, especially if ray tracing is enabled. The experience becomes smoother with minor reductions to ray tracing settings. Still, for an emerging GPU lineup like Intel Arc, reaching parity with established competitors in such a demanding title is a significant milestone.
Power Consumption and Efficiency (Cyberpunk 2077)
The TBP readings confirm that the Intel Arc B570 is effectively utilizing its available power to handle this heavy workload. In terms of performance-per-watt, the RTX 4060 leads the pack—thanks to the efficiency of DLSS FG—but the B570 edges out the RX 7600, showing solid energy efficiency for a GPU in its class.
The Last of Us Part 1 Performance Analysis
To further evaluate how the Intel Arc B570 performs in memory-intensive scenarios, we tested it in The Last of Us Part 1, a known VRAM-heavy title. Image quality was set to “Excellent” with FSR 3 (“Quality” mode) and frame generation enabled. Frame rates were measured during the intense opening sequence featuring a large crowd of NPCs and fast-paced action.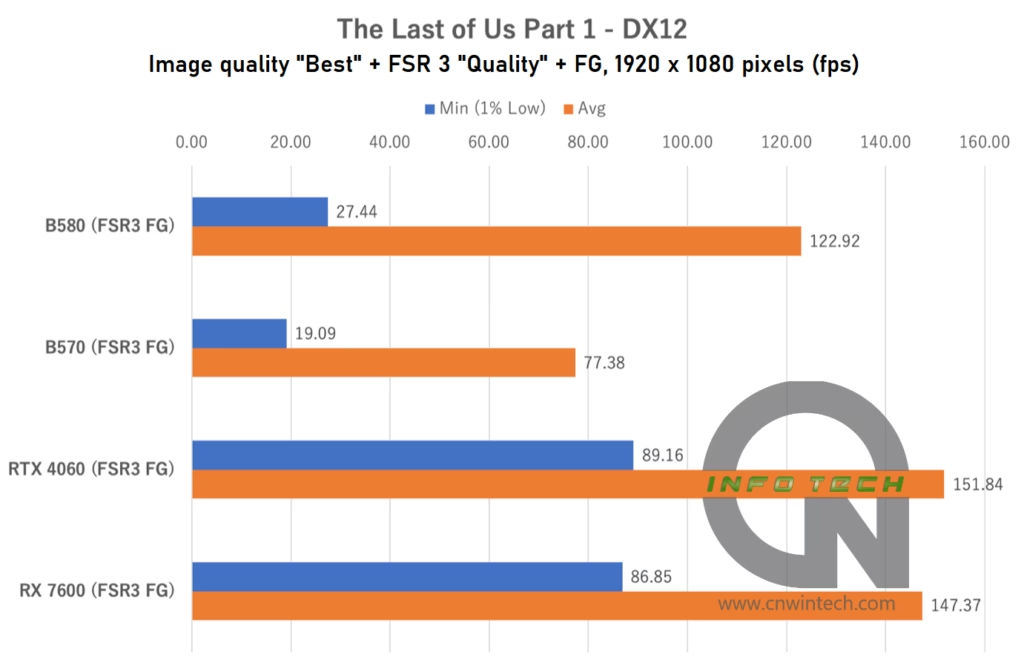
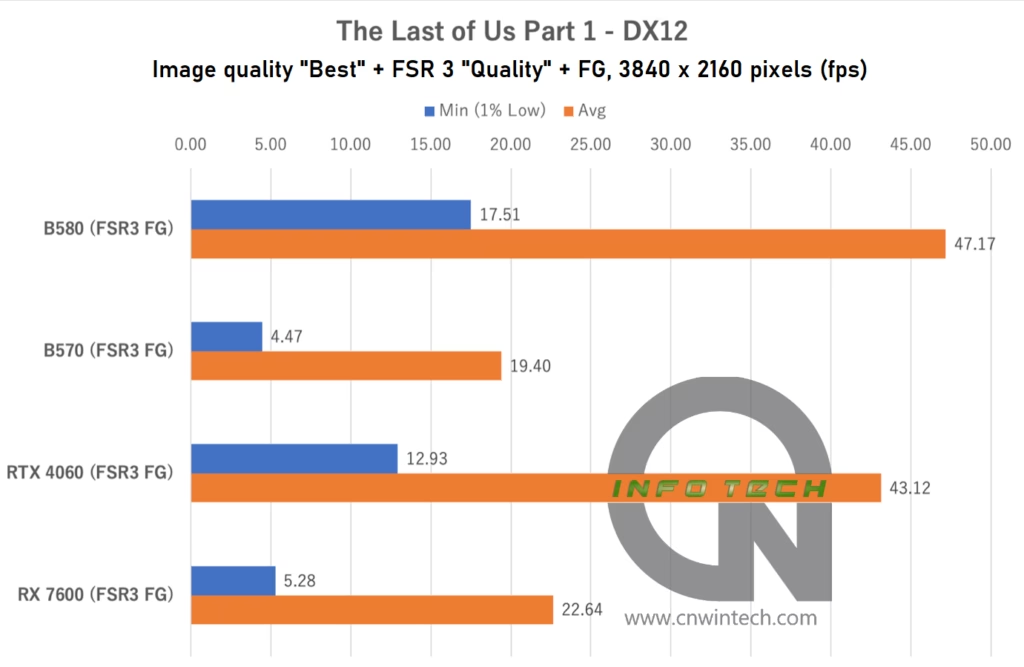
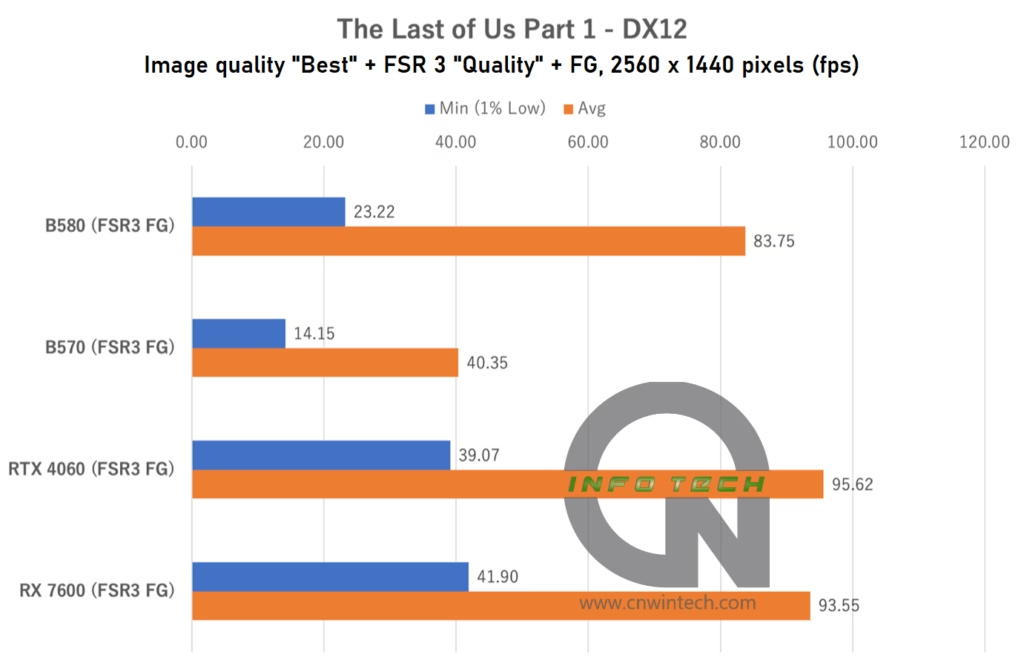
The Intel Arc B570 struggled significantly in this title, even at Full HD resolution. Frame rates dropped noticeably, indicating performance bottlenecks that weren’t as apparent in other games. At WQHD and above, playable performance becomes difficult to maintain unless graphical settings are dialed back.
Interestingly, both the RTX 4060 and RX 7600, despite having less VRAM, managed better average performance in this scenario. This suggests that driver optimizations and memory management remain areas where the Arc platform needs improvement.
While the B-series GPUs show marked progress over the previous A-series and appear more balanced in their capabilities, there are still too many titles where they fail to demonstrate their full potential. Continued investment in driver optimization and game-specific tuning will be key for Intel to position the Arc series as a “GPU with no blind spots”.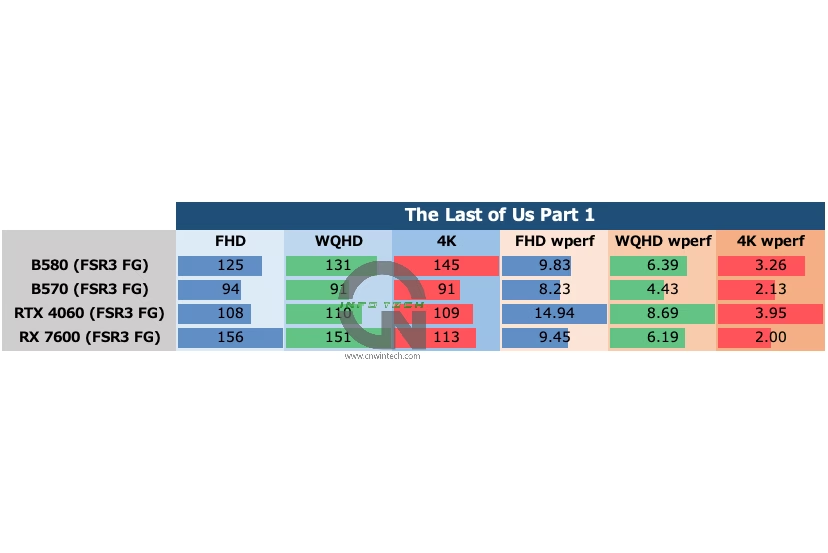
Power Consumption and Efficiency (The Last of Us Part 1)
Power consumption for the Intel Arc B570 plateaus just above 90W in this title, well below its typical load levels in other games. This indicates that the GPU isn’t being fully utilized, likely due to inefficiencies in how the game engine interacts with the driver stack or the way assets are loaded and processed.
BIOHAZARD RE:4 Performance Analysis
Moving into one of the most VRAM-demanding titles in our test suite, BIOHAZARD RE:4 pushes GPUs to their limits—even at Full HD resolution. For this benchmark, all image quality settings were maxed out, including ray tracing, and since frame generation (DLSS FG / FSR 3 FG) was not enabled, all GPUs used FSR 2 in “Quality” mode for consistency.
Frame rates were measured during exploration of the early-game village map—a visually dense environment with high-resolution textures, dynamic lighting, and complex enemy AI behavior.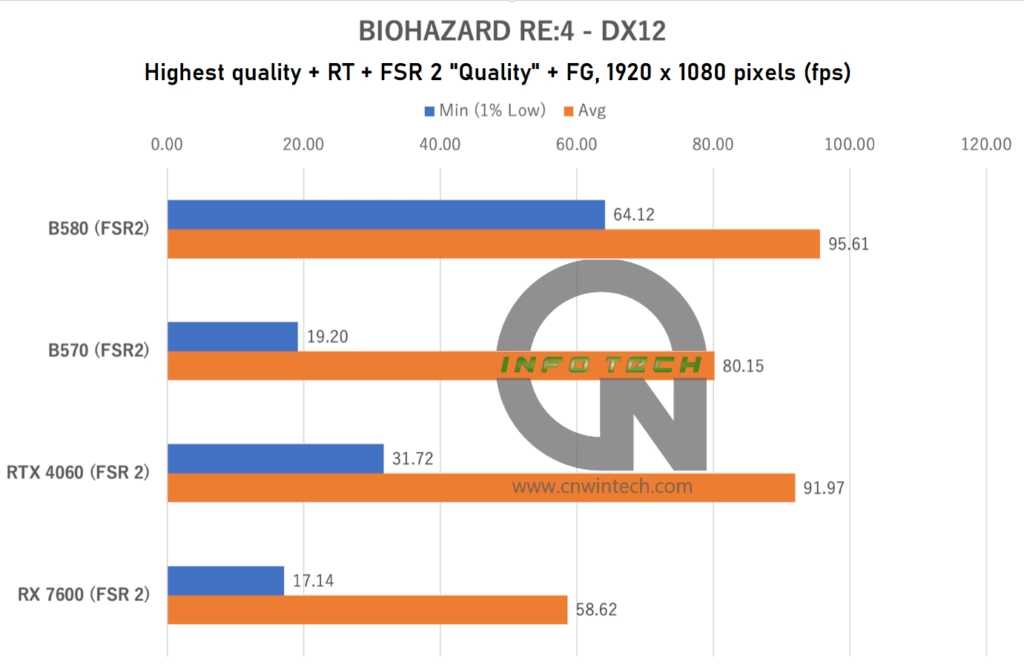
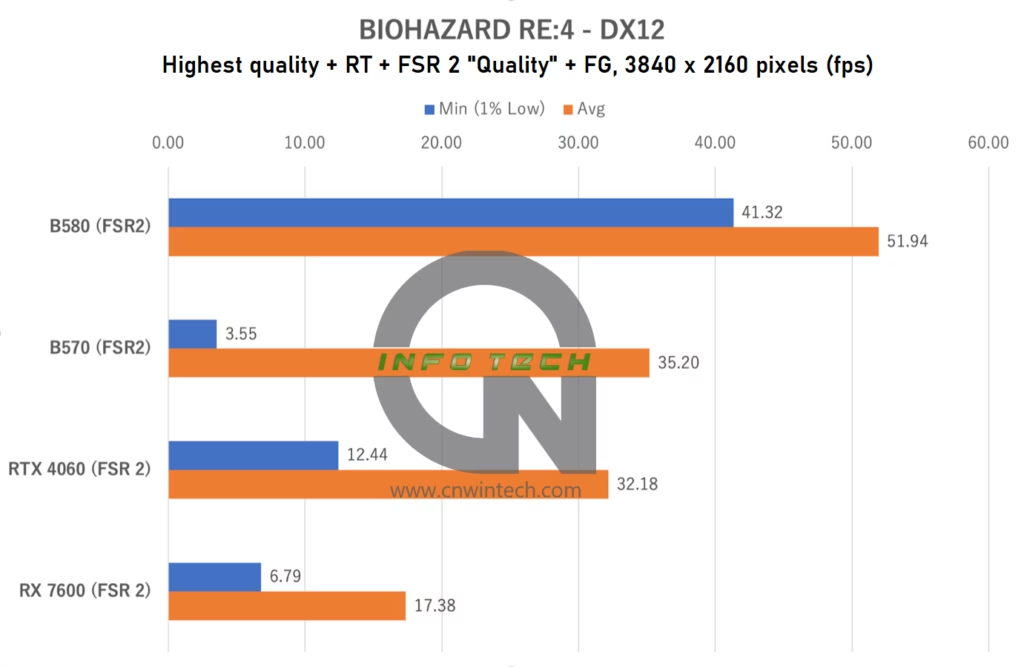
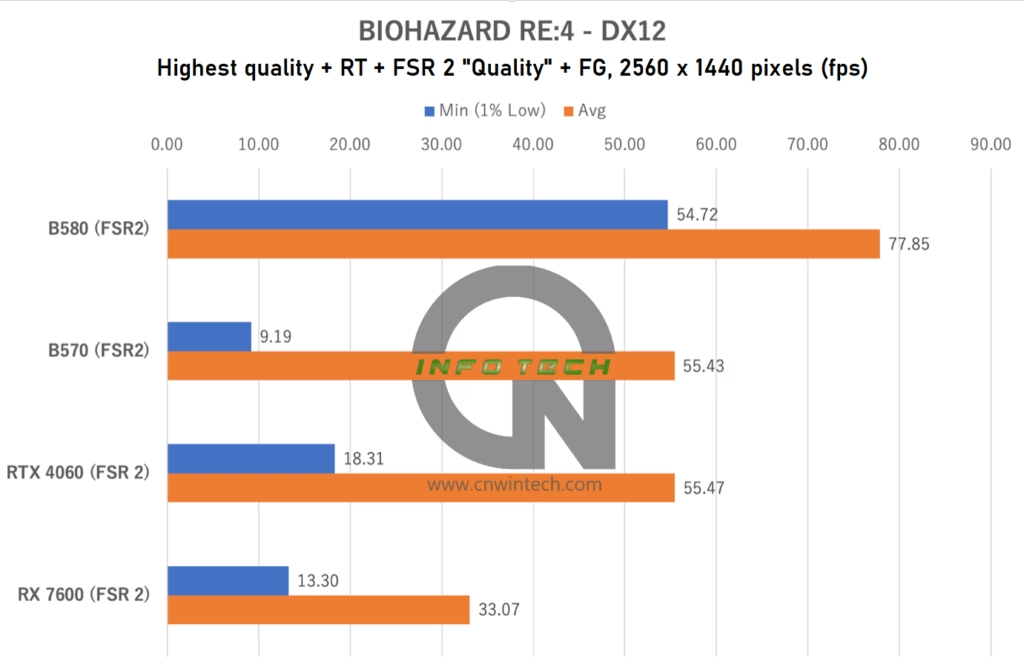
What stands out most in this title is not the average frame rate but rather the minimum frame rate, which serves as a strong indicator of gameplay smoothness. Both the RTX 4060 and RX 7600—equipped with only 8GB of GDDR6 VRAM—struggle significantly under these conditions, running out of memory even at 1080p and suffering from severe stuttering due to texture streaming issues and page faults.
The Arc B580, with its 12GB VRAM buffer, handles the workload much more gracefully, avoiding the worst of the stutter, something that deserves recognition. Unfortunately, the Intel Arc B570, with only 10GB of VRAM, falls into the same stutter-prone category as the 8GB cards, despite having a wider memory bus and better overall architecture.
Power Consumption and Efficiency (BIOHAZARD RE:4)
The Intel Arc B570 draws a respectable amount of power in this title, indicating active GPU utilization. However, the lack of meaningful performance gains suggests that the bottleneck lies not in compute capacity, but in VRAM bandwidth and capacity. In other words, while the GPU is working hard, it’s being held back by memory constraints.
S.T.A.L.K.E.R. 2: Heart of Chornobyl Performance Analysis
S.T.A.L.K.E.R. 2: Heart of Chornobyl continues the tradition of pushing hardware to its limits with ultra-detailed environments and heavy use of ray tracing. Image quality was set to “Ultra”, and DLSS/FSR 3 Frame Generation was enabled in “Quality” mode across supported platforms. Frame rates were captured during movement along a predefined path in the game’s first major base location.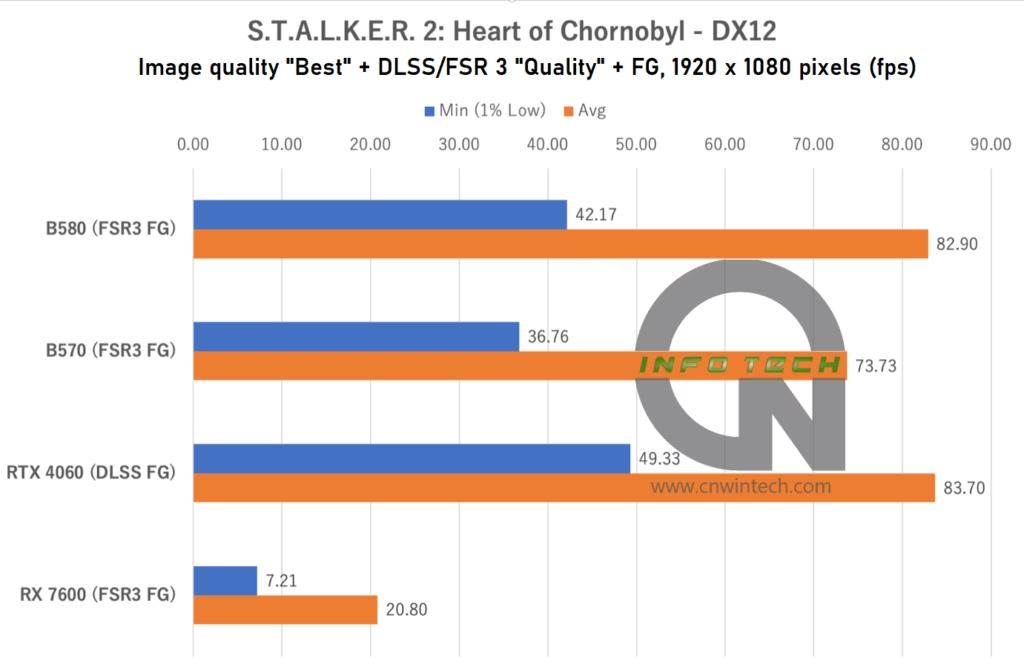
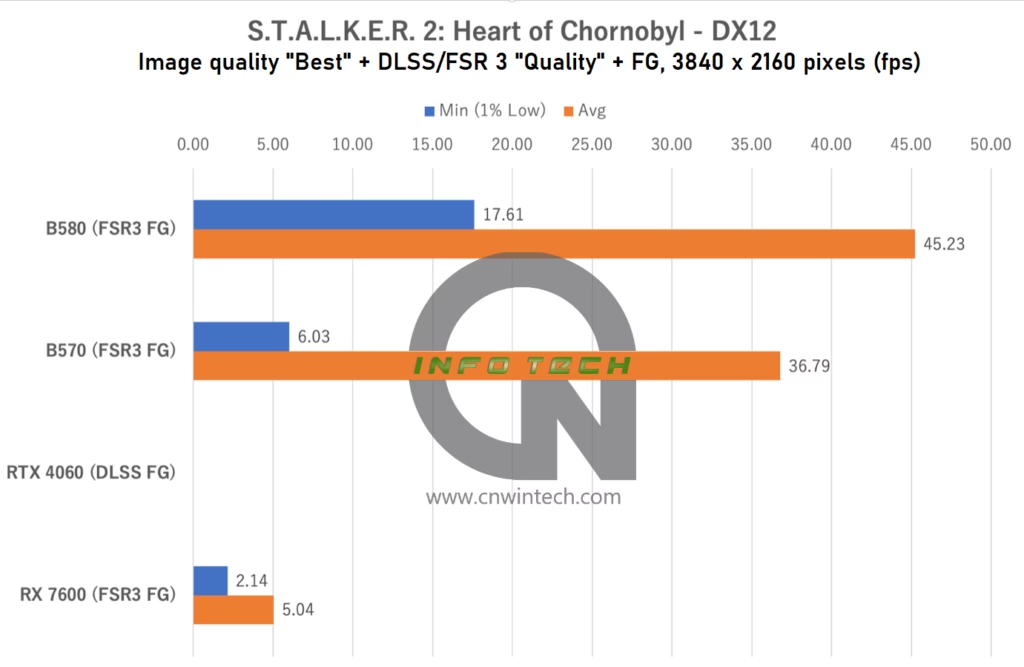
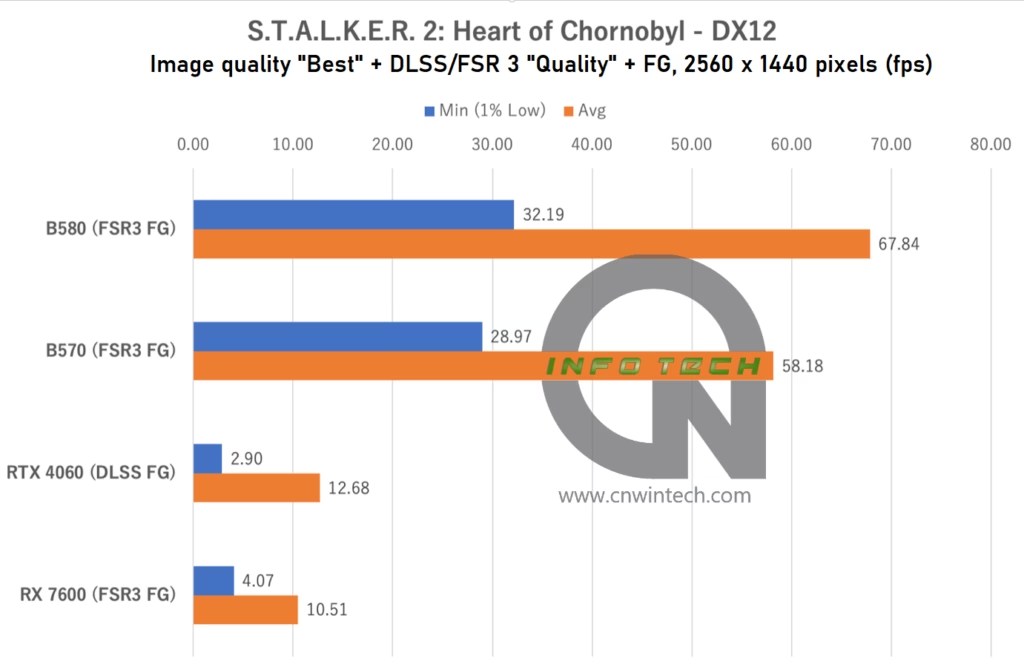
At Full HD, the RTX 4060 leads the pack, benefiting from the efficiency of NVIDIA’s DLSS stack. However, when resolution increases to WQHD, it begins to show signs of strain, likely due to VRAM limitations.
In contrast, the Intel Arc B-series shows consistent performance, with both the Intel Arc B570 and Intel Arc B580 maintaining competitive frame rates. While some minor stutter occurs, especially at higher resolutions, the overall experience remains playable without major dips. This makes S.T.A.L.K.E.R. 2 a clear showcase for the Arc lineup, where additional VRAM helps offset the game’s demanding asset load and memory usage.
That said, real-world playability benefits from dialing back image quality by one or two levels, especially if smoothness is prioritized over absolute visual fidelity.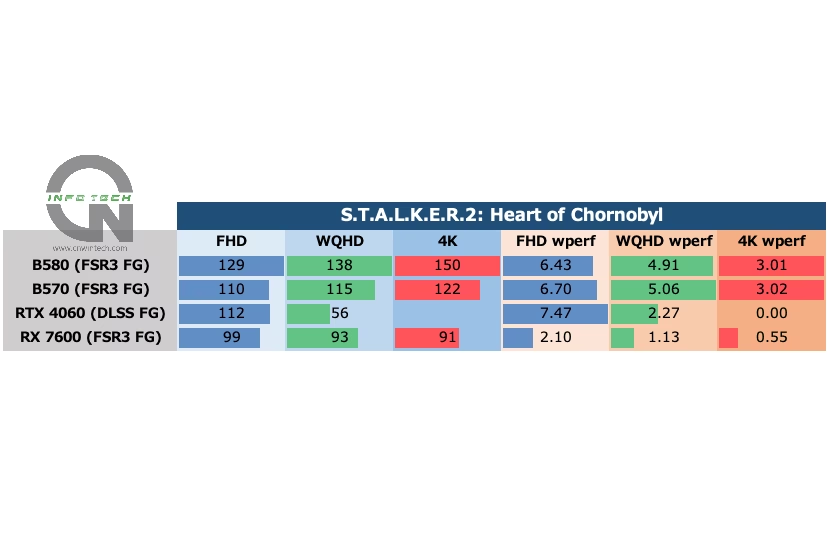
Power Consumption and Efficiency (S.T.A.L.K.E.R. 2)
Despite delivering relatively high frame rates, the Intel Arc B570 consumes only around 110–120W in S.T.A.L.K.E.R. 2, suggesting there may still be untapped headroom in terms of performance potential. This also points to possible inefficiencies in how the driver schedules workloads or how the game interacts with Intel’s software stack.
Indiana Jones and the Great Circle Performance Analysis
Indiana Jones and the Great Circle, developed by MachineGames and published by Bethesda, features a unique approach to upscaling technology, unusual for a modern AAA title. Rather than allowing third-party solutions like FSR or XeSS, the game only supports NVIDIA’s DLSS and DLSS Frame Generation natively, limiting options for AMD and Intel users.
For this test, image quality was set to “Ultra” but under these settings, the RTX 4060 failed to launch the game entirely, likely due to driver or compatibility issues. Lowering the image quality allowed the game to run smoothly on the RTX 4060, but it disqualified it from our “Ultra” benchmark testing.
All other GPUs used a game-side static render scale of 67% (effectively a fixed-resolution upscaler), as no hardware-based upscaling was available. Frame rates were measured during movement along a predefined path in the iconic Castel Sant’Angelo map.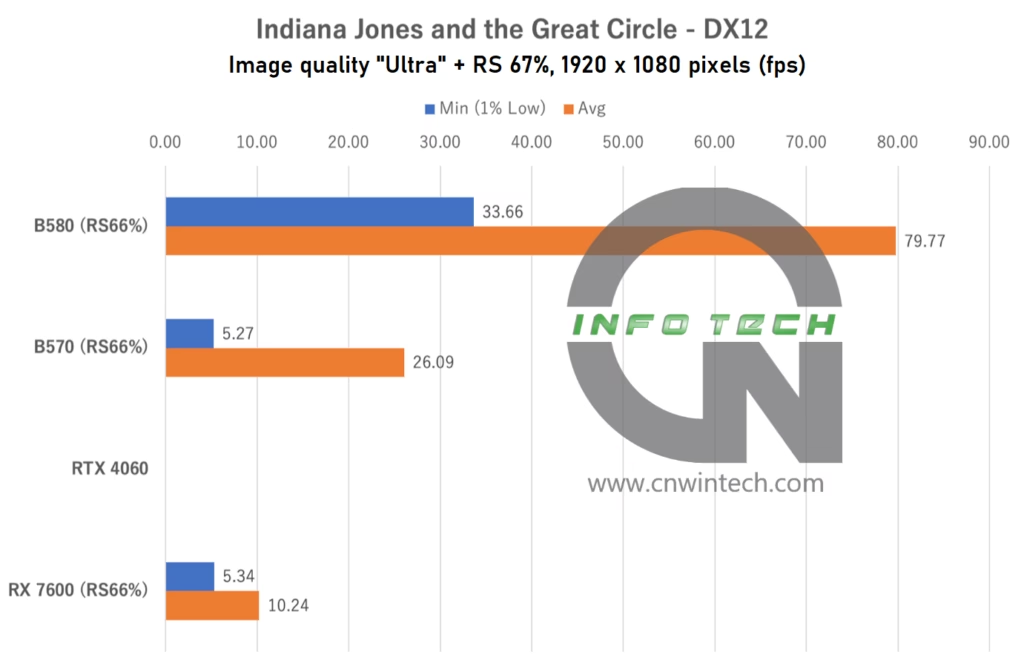
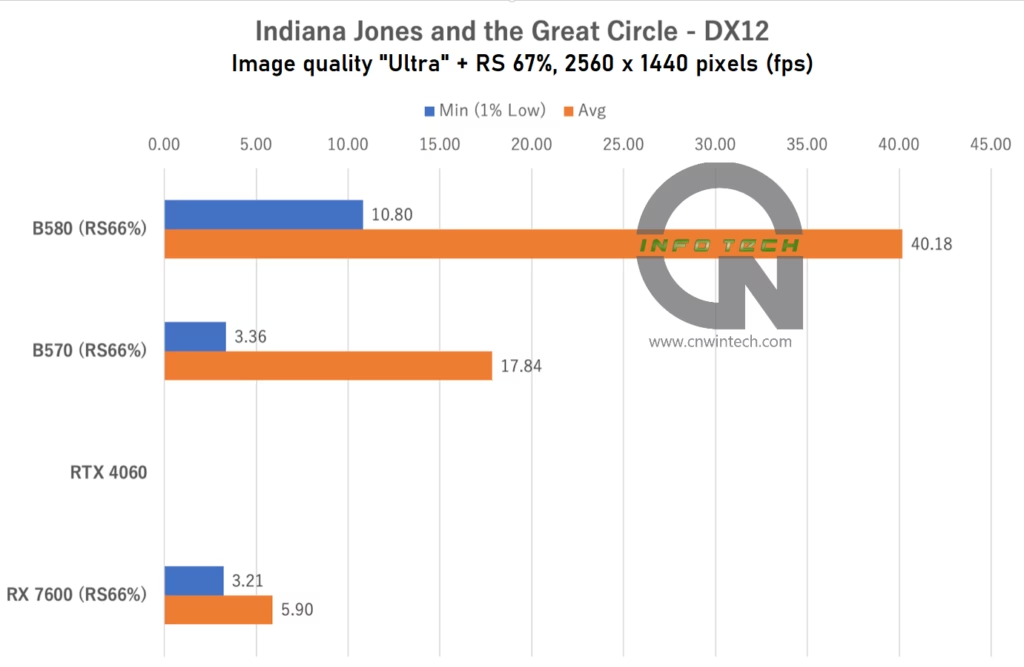
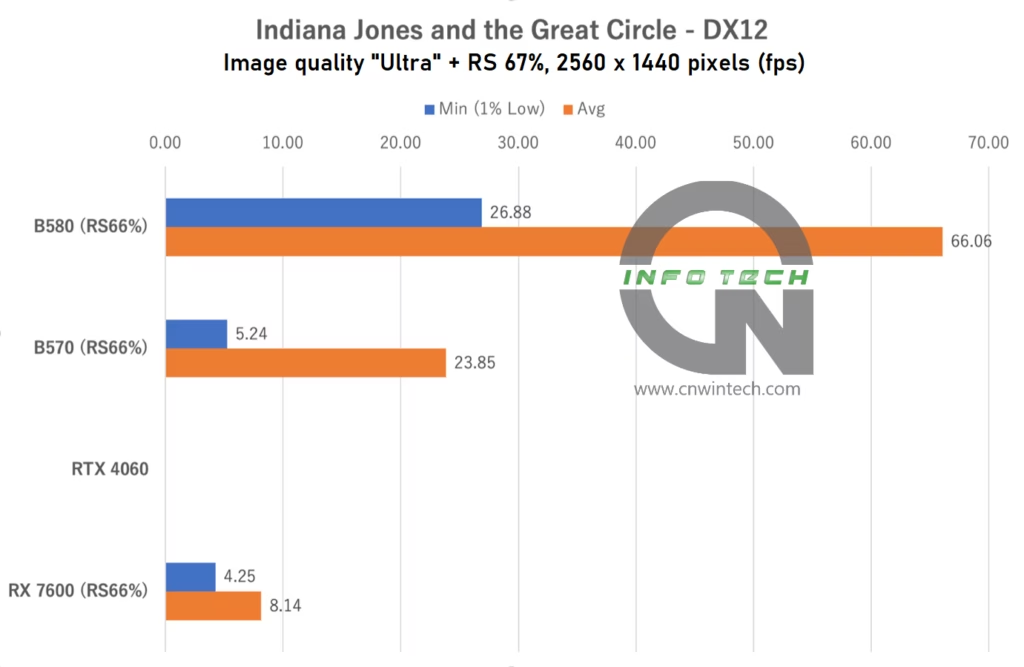
The RX 7600, despite having only 8GB of VRAM, managed to run the game, albeit with marginal performance, making actual gameplay feel sluggish. Meanwhile, the Arc B580 offered a relatively smooth experience at Full HD, and while WQHD felt heavier, it remained playable for exploration purposes.
In contrast, the Intel Arc B570—with its 10GB VRAM and narrower 160-bit memory bus—delivered only about half the frame rate of the B580. Given the game’s heavy use of ray tracing and high-resolution assets, the limitations in both VRAM capacity and bandwidth became evident.
Power Consumption and Efficiency (Indiana Jones and the Great Circle)
The performance gap between the Intel Arc B580 and Intel B570 is also reflected in their power consumption profiles. The Intel Arc B580 actively utilizes its GPU resources to deliver acceptable frame rates, while the Intel Arc B570 appears largely underutilized, suggesting that performance is being bottlenecked before the GPU can reach full capacity.
This is especially noticeable when compared to the RX 7600, which, although not optimal, showed better scaling and utilization despite similar VRAM constraints.
Final Thoughts: The Role of the Intel Arc B570 in the Lineup
With the conclusion of our Indiana Jones and the Great Circle testing, we wrap up our evaluation of the Intel Arc B570 across 10 major titles. While the card performed admirably in select games like Marvel Rivals, where XeSS FG provided a significant performance boost, it struggled in others, such as BIOHAZARD RE: 4 and Starfield, where VRAM and memory bandwidth limitations severely impacted real-world usability.
Overall, the Intel Arc B570 often ended up in a gray zone, offering little tangible advantage over existing 8GB VRAM GPUs like the RTX 4060 and RX 7600, especially at higher resolutions or in content-heavy scenarios.
At a price point just around $33 USD below the B580, many consumers may find it more compelling to invest in the B580 instead. With its 12GB VRAM and wider 192-bit memory bus, the B580 consistently delivered smoother performance across demanding titles, earning recognition as a legitimate “third force” among consumer GPUs.
On the other hand, the Intel Arc B570 seems best viewed as a complementary option to the Intel Arc B580 rather than a standalone competitor. It’s reduced VRAM and narrower bus limit its appeal unless matched by a significantly lower price.
Currently, the entry-level RTX 4060 retails around $280 USD, with the RX 7600 priced slightly lower at around $260 USD. If the Intel Arc B570 hopes to carve out a space in this market, it must either undercut these prices substantially or highlight alternative strengths beyond raw gaming performance, such as superior video encoding capabilities through Intel’s dedicated media engines.
Ultimately, the Arc series has made clear strides since its early days, particularly in terms of stability and feature completeness. However, continued focus on driver optimization and reducing the number of games where performance doesn’t reflect hardware potential will be key for Intel in building lasting user confidence.
If done right, the Arc lineup could evolve into a trusted choice for users seeking a well-rounded GPU with few blind spots—a true generalist in a market increasingly dominated by specialists.
Summary
The Intel Arc B570 Challenger 10GB OC represents a meaningful step forward for Intel’s discrete GPU lineup. It proves that the company can deliver a functional, mid-range card capable of competing in modern games, especially those with good driver support and XeSS integration.
However, its memory constraints, inconsistent performance, and tight pricing relative to competitors make it a harder sell unless you’re specifically looking to support Intel’s ecosystem or benefit from its unique features like AV1 encoding and XeSS FG.
For most gamers, the Intel Arc B580 offers a smoother, more future-proof experience, while the RTX 4060 and RX 7600 remain stronger all-around options in this price range. That said, the B570 still has a place, as a secondary choice or stepping stone toward full maturity in the Arc series.
Do you think you have other ideas about the Pros and Cons of Intel Arc B580’s VRAM and Memory Bus Width Adjustments? You can comment below or discuss more related to Pros and Cons of Intel Arc B580’s VRAM and Memory Bus Width Adjustments in the CnwinTech Forum. Also, read more articles about Insurance Tech, Insurance Business Investment, or other exciting tech tips and tricks at CnwinTech.
Score Assessment
Performance - 7.8
Facilities & Features - 8.2
Design & Easiness - 8.5
Price - 6.5
7.8
Overall
Pros: +Competitive Performance with XeSS FG Support. +Improved Driver Stability and Feature Set. +Better Power Efficiency at High Resolutions. +VRAM Advantage over 8GB Competitors. +Ideal Complement to the B580. Cons: -Performance Lags Behind B580 and Competitors in Many Titles. -Memory Bottlenecks at Higher Resolutions. -Inconsistent Real-World Performance Across Games. -Power Consumption Doesn’t Always Reflect Utilization. -Pricing Reduces Value Proposition Against Alternatives.











